Introduction
India is currently undergoing its general election, the largest democratic exercise in the world. The nation’s political landscape is abuzz with activity as major parties like the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, and the Indian National Congress (INC), helmed by Rahul Gandhi, vigorously campaign across this vast country.
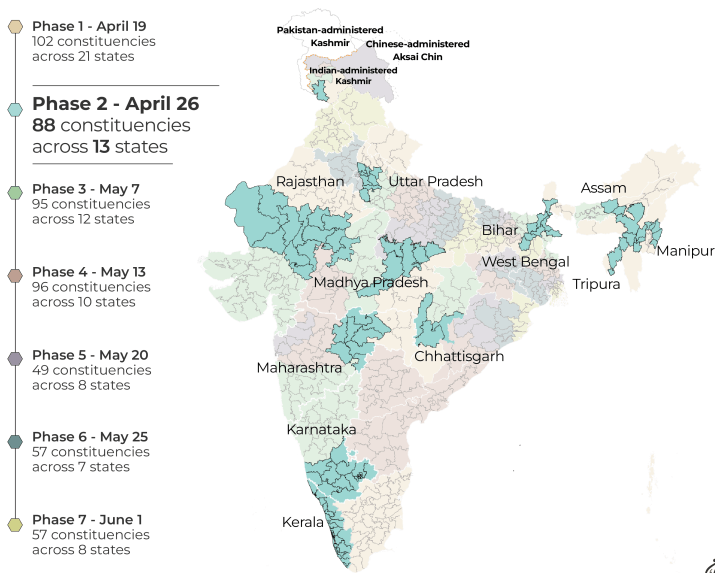
Campaign Dynamics
Recent trends in the election highlight a surge in cross-party movements and alliances, significant defections, and the introduction of new candidates, all reshaping the electoral landscape. High-profile movements include notable leaders switching allegiances and emerging figures in political hotspots, reflecting the volatile and dynamic nature of Indian politics. Leaders such as Narendra Modi and Rahul Gandhi are pivotal in driving their respective party campaigns, emphasising themes central to their political agendas.
Electoral Process and Innovations
The logistical scale of India’s elections is unprecedented with over 969 million voters participating through millions of electronic voting machines across diverse and challenging terrains. The Election Commission of India has implemented rigorous measures to ensure inclusivity and fairness, deploying vast resources to accommodate all eligible voters.
Impact of the Election
The outcome of this election is poised to significantly influence India’s future policies and its standing on the global stage. Key issues at stake include economic reforms, national security, and social justice, which are crucial to the nation’s development trajectory.
Conclusion
As the world watches, India’s democratic spirit is vibrantly displayed in an election that not only decides its leaders but also tests the robustness of its democratic institutions.
Further Resources
- Learn more about the election process and updates here.
- For detailed voter information and services, visit the Indian Government’s Voter Information Services.
- Explore historical and contextual details of the 2024 Indian Lok Sabha elections at Encyclopædia Britannica.